Uterine fibroids are known to have an impact in a woman’s ability to conceive naturally or even with IVF treatments. In this section, we talk about uterine fibroids and their effects on fertility and the specific ways that they can contribute to female infertility. If a woman has fibroids that can potentially impair her fertility, then removal of the fibroid may be necessary in order to achieve pregnancy.
Uterine fibroids are muscular tumors that form in the wall of the womb. The universal medical term used for fibroids is “myoma”. Most of these tumor growths are non-cancerous and most women will have fibroids in the uterus without even noticing them.
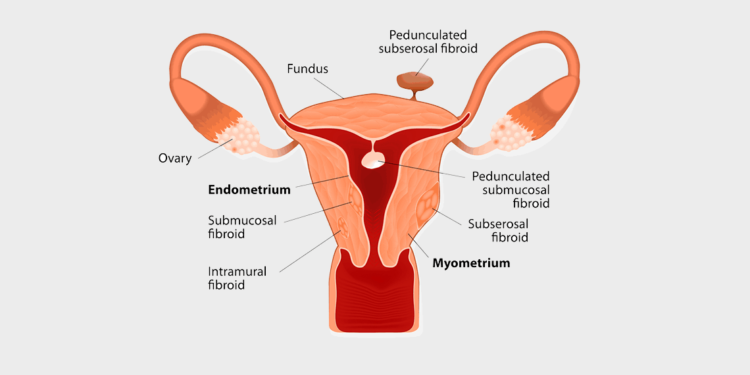
Fibroids can be a single growth or there can be numerous small tumors in the uterus. The size of a fibroid can be as small as a melon seed or as big as a small melon. The larger the fibroid, the more problems it is likely to cause in the uterus regarding a woman’s ability to conceive. It is not only the size of the fibroid that can affect a woman’s ability to achieve pregnancy, but also the localization.
Fibroids are classified in three major categories based on their precise locations:
1- Submucosal fibroids: These are the types of fibroids that grow in the uterine cavity
2- Intramural fibroids: These are the fibroids that grow within the wall of the uterus
3- Subserosal fibroids: These are the fibroids that grow on the outside of the uterus.
Fibroids that are in the uterine cavity are the main types of fibroids that have a direct association with infertility. These fibroids can indent the cavity or pressurize the endometrium, therefore, directly affecting embryo implantation. However, other fibroids can also negatively affect chances of conception due to their sizes.
How Do Fibroids Cause Infertility?
– Fibroids located above the cervix can change its position and therefore restrict passage of sperm cells that can travel through the cervix.
– Certain fibroids can block the fallopian tubes, thus restricting oocyte movement and fertilization.
– Some fibroids can restrict the blood flow into the uterine cavity, where the embryo would normally implant and generate a pregnancy.
– Fibroids can also possibly cause changes in the uterine muscle that prevents embryo movement.
How do I know if I have a fibroid?
Fibroids can sometimes have certain symptoms while sometimes they may go unnoticed for years. A proper diagnosis requires a consultation with your gynecologist so that proper diagnosis measures can be used. However, it will be important to know about some of the symptoms of fibroids:
– Heavy bleeding and/or painful menstrual periods
– Feelings of fullness in the pelvic region
– Pain during sex
– Frequent urination
– Lower back pain
– Infertility and/or pregnancy losses
While not all the fibroids will impair your ability to achieve and maintain a healthy pregnancy, it is always a good idea to see your gynecologist at certain time intervals for routine testing and scans so that problems in the uterus do not go unnoticed.